Notifications Android
Configure Push notifications.
All the public APIs in the SDK should be called after initializing the SDK via HelpshiftSdk.install() API
Configure push notifications via Helpshift
Helpshift enables you to send notifications to your users. This is particularly useful when you have multiple users on multiple platforms like iOS and Android. Notifications are useful to tell your users when you reply to an issue that they submitted. When the app is backgrounded, the notification that is sent from Helpshift appears as a notification.
To know more about the FCM Push, refer:- Firebase Cloud Messaging
Prerequisites
Implement FCM push in your app.
For FCM, refer to the Firebase Cloud Messaging documentation.
Configure Helpshift Agent Dashboard
To enable the Helpshift system to send push notifications to your users you will have to add an Android as a platform in your app (if you have not added already). And then click on the push notifications option.

Enter your FCM key credentials per app, via the Settings page > App listing in the left navigation > Scroll down to Push Notifications settings section for the app.
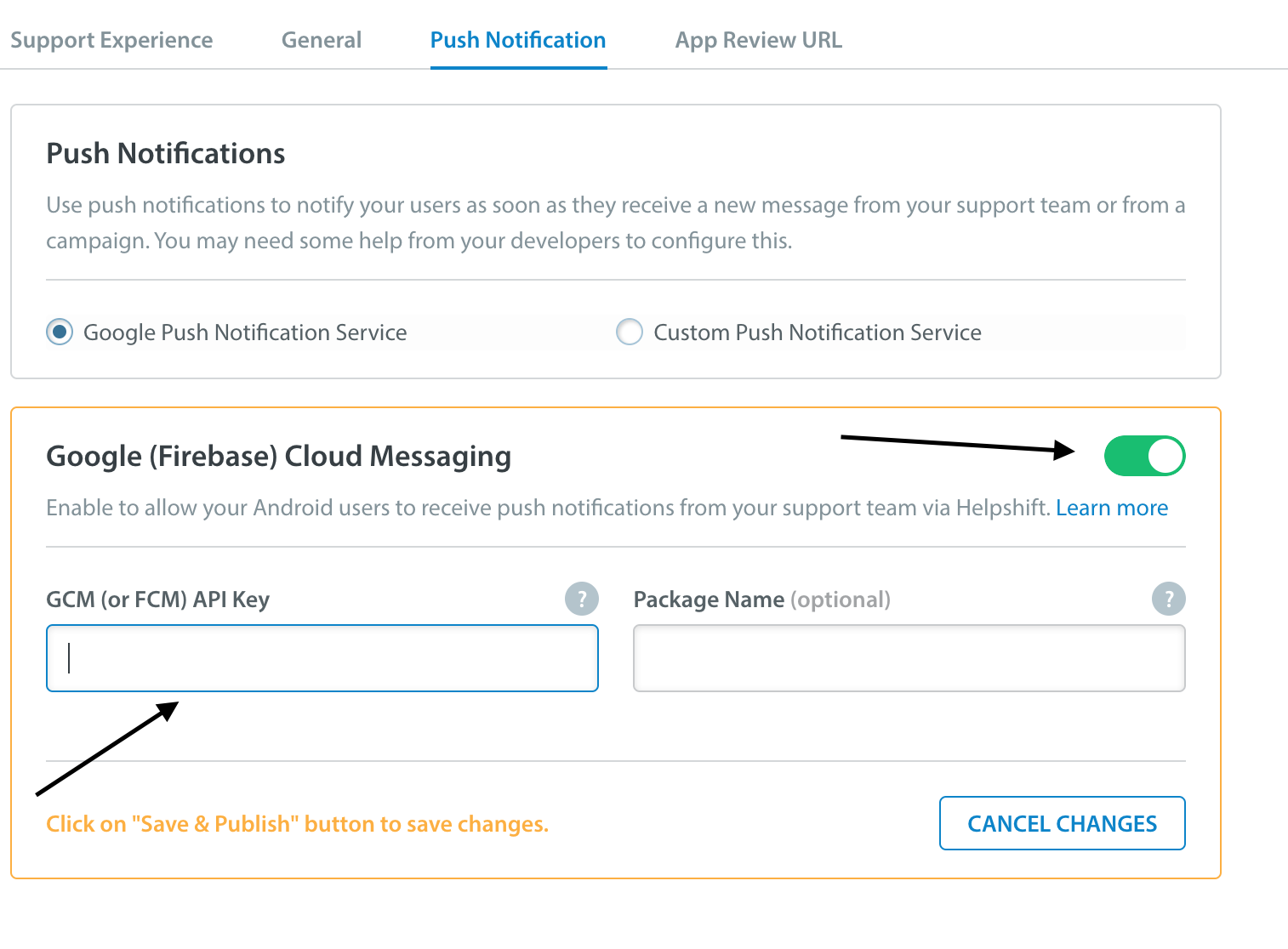
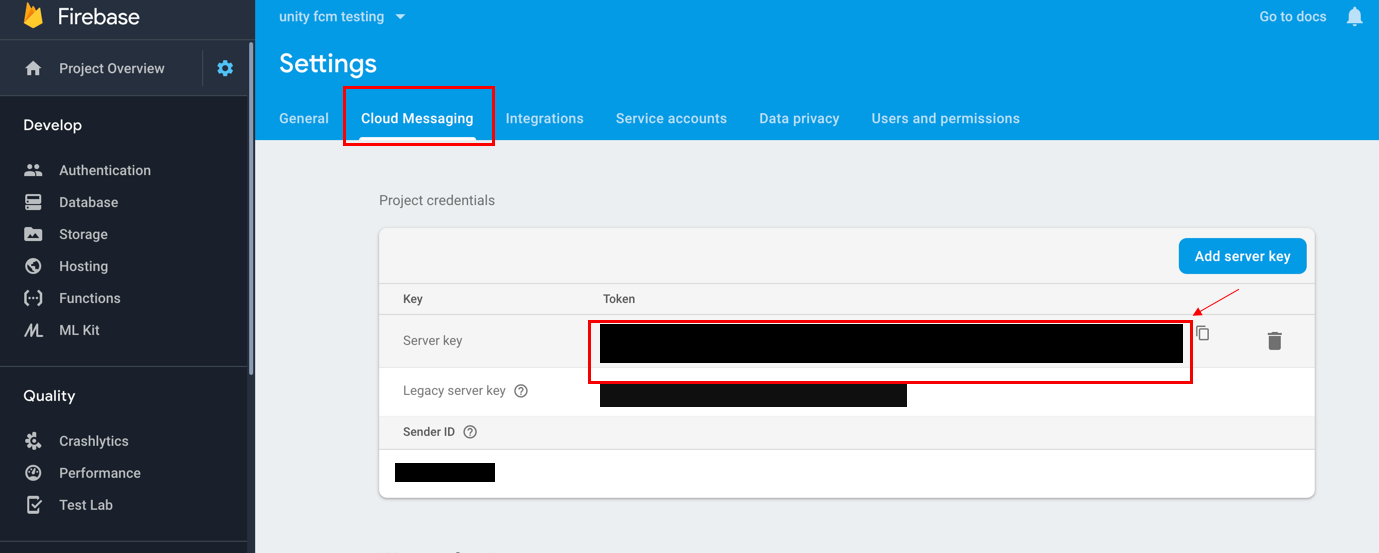
For FCM users, the API key can be found at your Firebase API Console
Configure the Helpshift Unity SDK to handle notifications
Push notifications
Configure FCM push notification plugins {#}
Before you begin
- Integrate FCM Unity Android plugin as documented here: Firebase Cloud Messaging Guide
If you have already integrated push notifications, Use the HelpshiftSdk.RegisterPushToken(string deviceToken) API to register the device token with the Helpshift SDK. Helpshift can now start sending push notifications to your app.
Once this is done, you can use the HelpshiftSdk.HandlePushNotification(Dictionary<string, object> pushNotificationData) API to send the payload received in the notification.
To check whether this notification is being sent from the Helpshift's push notification service, please check the origin field of the notification. If it is "helpshift, the notification is a Helpshift notification.
public void OnTokenReceived(object sender, Firebase.Messaging.TokenReceivedEventArgs token) {
HelpshiftSdk.GetInstance().RegisterDeviceToken (token.Token);
}
public void OnMessageReceived(object sender, Firebase.Messaging.MessageReceivedEventArgs e) {
IDictionary<string, string> pushData = e.Message.Data;
if (pushData.ContainsKey ("origin") && pushData ["origin"].Equals ("helpshift")) {
Dictionary<string, object> hsPushData = new Dictionary<string, object>();
foreach (string key in pushData.Keys) {
hsPushData.Add (key, pushData [key]);
}
HelpshiftSdk.GetInstance().HandlePushNotification (hsPushData);
}
}
If your application is not running and it receives a push notification then it will start the application in background (by invoking the push notification receiver registered in java). In this case, UnityEngine might not be initialized and the C# api HelpshiftSdk.HandlePushNotification might not be useful.
If you are unable to delegate the push notification payload from the Java receiver class to C# api's then, for such cases, you can use the native Java api HelpshiftUnity.handlePush(Context context, Intent intent) to handle push notifications from Helpshift.
In Java implementation of the receiver for push notifications, you can use this api as in the following example.
public class HelpshiftCustomFCMService extends ListenerService {
private static final String TAG = "Helpshift Native";
@Override
public void onMessageReceived(RemoteMessage message) {
String from = message.getFrom();
Map<String, String> data = message.getData();
Log.d(TAG, "onMessageReceived, from: " + from + ", data: " + data);
String origin = data.get("origin");
if (origin != null && origin.equals("helpshift")) {
Log.d(TAG, "Helpshift Notification received");
// Handle push with native Helpshift java apis directly.
HelpshiftUnity.handlePush(this, data);
} else {
Log.d(TAG, "Notification from non-helpshift service");
// Call super to forward the notification to the default FCM service.
super.onMessageReceived(message);
}
}
}
Refer the sample project for FCM Unity plugin integration with Helpshift SDK here.
Note: The latest FCM plugin for Unity uses androidx libraries. For updating the Helpshift Unity SDK X reference to androidx libraries please follow the steps here.
Configure Other push notification plugins
If you are using any third party plugin for push notifications. you can use HelpshiftSdk.RegisterPushToken(string deviceToken) API to register the device token and HelpshiftSdk.HandlePushNotification(Dictionary<string, object> pushNotificationData) API to send the payload received in the notification.
The following is an example to register device token:
void registrationSucceededEvent( string registrationId )
{
Debug.Log( "registrationSucceededEvent: " + registrationId );
HelpshiftSdk.GetInstance().RegisterPushToken(registrationId);
}
Once this is done, you can use the HelpshiftSdk.GetInstance().HandlePushNotification(Dictionary<string, object> pushNotificationData) API to send payload which you receive in the notificationReceivedEvent callback in your plugin.
To check whether this notification is being sent from the Helpshift's push notification service, please check the origin field of the notification. If it is "helpshift", the notification is a Helpshift notification.
In-app notifications
In-app notifications are similar to notifications in the notification drawer . Unlike push notifications, they appear only when you app is running.
These notifications are sent when an agent replies to a customer's issue. Your customers can go straight into the conversation screen when they tap on the notification.
If the FCM device token is registered for push notifications, then in-app notifications will be disabled. In-app notifications are disabled to avoid duplicate notifications from both push notifications and in-app notifications.
Showing notification count when replies are sent to the user
To fetch unread messages count from the server you can call Helpshift.RequestUnreadMessageCount(shouldFetchFromServer) API. This API will return unread messages count via delegate.
Based on the value of shouldFetchFromServer, the locally stored count will be returned if shouldFetchFromServer is false else from the server by fetching remotely when shouldFetchFromServer is true. An example use of this count is to update the badge count to indicate unread messsages. Please note that before calling this method, you need to set the listener for Helpshift events by calling the Helpshift.SetHelpshiftEventsListener(eventsListener) API.
// Requesting unread count
private void RequestUnreadCount()
{
Helpshift.RequestUnreadMessageCount(true);
}
When you call this API, you receive the unread count in your event listener which implements IHelpshiftEventsListener.
Following is an example implementation
public class HSEventsListener : IHelpshiftEventsListener
{
// ...
public void HandleHelpshiftEvent(string eventName, Dictionary<string, object> eventData)
{
if(eventName.Equals(HelpshiftEvent.RECEIVED_UNREAD_MESSAGE_COUNT))
{
Debug.Log("Unread count: " + eventData[HelpshiftEvent.DATA_MESSAGE_COUNT]);
Debug.Log("Is Unread count from cache: " + eventData[HelpshiftEvent.DATA_MESSAGE_COUNT_FROM_CACHE]);
// Do something with the unread count here, for example, update the badge count.
}
}
//...
}
- The notification count is fetched via this API from the SDK cache and Helpshift's servers (indicated by the value of
fromCachein the example above). However, the count from Helpshift’s servers is rate limited and it returns the value only if a subsequent call is made to the API, after the reset timeout or when the user just closes the chat screen (whichever is earlier). For an active issue, the reset timeout is 1 minute and 5 minutes for inactive issues.